Matplotlib
Contents
Matplotlib#
Author: Fu Yin
Update: August 6, 2022
Reading: 30 min
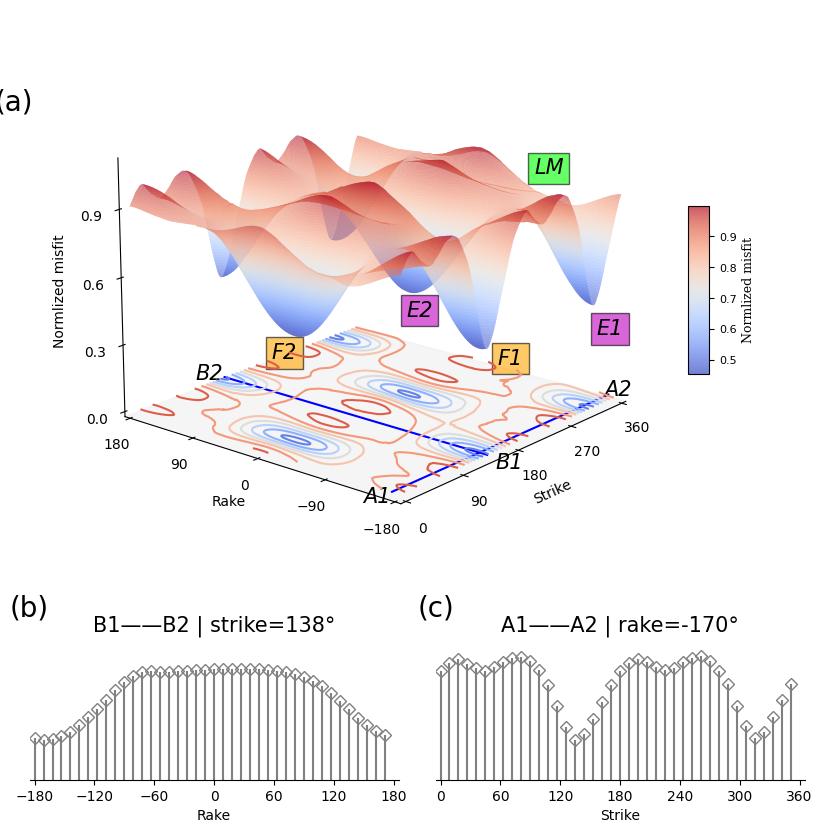
3D Misfit Space#
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue May 25 22:44:49 2021
@author: yf
"""
import numpy as np
import os
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.pyplot import MultipleLocator
import math
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib import cm
#%% 1. input parameter
rank_path = "./matplotlib_files/3d-mcmtpy/"
MPI_n = 30
strike_num = 361 # step:5度 = 73 || step:1度 = 361
rake_num = 361
Strike = 138 # rake 剖面时,选取strike的数值
Rake = -170 # strike 剖面时,选取rake的数值
Num_stem = 40
#%% 2. read data
for i in range(0, MPI_n, 1):
FM_all_path = os.path.join(rank_path, 'rank_'+str(i)+'_FM_all')
if i == 0:
FM_all = np.loadtxt(FM_all_path)
else:
FM_all = np.vstack((FM_all, np.loadtxt(FM_all_path)))
misfit_all = FM_all[:, 0]
mag_all = FM_all[:, 1]
strike_all = FM_all[:, 2]
dip_all = FM_all[:, 3]
rake_all = FM_all[:, 4]
depth_all = FM_all[:, 5]
index_min = np.where(misfit_all == np.min(misfit_all))[0]
fm_min = FM_all[index_min] # 全局最小值
strike = np.linspace(0, 360, strike_num) # strike_all
rake = np.linspace(-180, 180, rake_num) # rake_all
X, Y = np.meshgrid(strike, rake)
Z = misfit_all.reshape((strike_num,rake_num))/max(misfit_all) # 此时需要转置才能对应xy平面
Z=Z.T
for i in range(0, strike_num, 1):
if (strike[i] <= Strike) and (strike[i+1] > Strike):
strike_index = i
for i in range(0, rake_num, 1):
if (rake[i] <= Rake) and (rake[i+1] > Rake):
rake_index = i
rake_2D = Z[ :,strike_index] # rake 二维剖面的数组
strike_2D = Z[ rake_index,:] # strike 二维剖面的数组
#%% 3. plot
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
gs1 = gridspec.GridSpec(4, 2)
# fig.suptitle('Strike and Rake Grid-Search')
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.1, hspace=0.5)
# 3.1. 3-D subplot
cmap = 'coolwarm' # coolwarm plasma viridis
ax = plt.subplot(gs1[:-1, :], projection='3d')
# plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Times New Roman']
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap=cmap, shade=True, antialiased=True, rstride=1, cstride=1, alpha=0.7)
ax.contour(X, Y, Z, zdir='z', offset=0, cmap=cmap)
ax.set_xlim(0, 360)
ax.set_ylim(-180, 180)
ax.set_zlim(0, 1.1)
ax.set_xlabel('Strike')
ax.set_ylabel('Rake')
ax.zaxis.set_rotate_label(False) # 必须禁用z轴标签的自动旋转
ax.set_zlabel('Normlized misfit', rotation=90)
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(90) # 坐标刻度间隔
y_major_locator=MultipleLocator(90)
z_major_locator=MultipleLocator(0.3)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator)
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(y_major_locator)
ax.zaxis.set_major_locator(z_major_locator)
ax.grid(False) # 关闭网格
# ax.invert_xaxis() # 反转x轴
ax.xaxis.set_pane_color((1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0)) # x 面的背景色设置为透明
ax.yaxis.set_pane_color((1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0)) # y 面的背景色设置为透明
ax.view_init(elev=18, azim=220) # 20 60
# ax.set_axis_off()
# ax.set_xticks([])#不显示x坐标轴
# ax.set_yticks([])#不显示y坐标轴
# ax.set_zticks([])#不显示z坐标轴
# colorbar
cb=fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.3, aspect=8)
font = {'family' : 'serif',
'color' : 'black',
'weight' : 'normal',
'size' : 9,
}
cb.set_label('Normlized misfit',fontdict=font)
cb.ax.tick_params(labelsize=8) # colorbar 标签字体大小
# text
ax.text(190, -168, 0.35, 'F1', style='italic', fontsize=15,verticalalignment='center',
horizontalalignment='center',bbox = dict(facecolor = "orange", alpha = 0.6))
ax.text(30, -4, 0.4, 'F2', style='italic', fontsize=15,verticalalignment='center',
horizontalalignment='center',bbox = dict(facecolor = "orange", alpha = 0.6))
ax.text(260, -160, 1.1, 'LM', style='italic', fontsize=15,verticalalignment='center',
horizontalalignment='center',bbox = dict(facecolor = "lime", alpha = 0.6))
ax.text(360, -170, 0.30, 'E1', style='italic', fontsize=15,verticalalignment='center',
horizontalalignment='center',bbox = dict(facecolor = "m", alpha = 0.6))
ax.text(250, 0, 0.35, 'E2', style='italic', fontsize=15,verticalalignment='center',
horizontalalignment='center',bbox = dict(facecolor = "m", alpha = 0.6))
# 画两条横线
ax.plot(strike,Rake*np.ones(shape=strike.shape) , zs=0, zdir='z',color='b')
ax.text(-20, -168, 0,'A1', style='italic', fontsize=15,verticalalignment='center',horizontalalignment='center')
ax.text(380, -168, 0,'A2', style='italic', fontsize=15,verticalalignment='center',horizontalalignment='center')
ax.plot(Strike*np.ones(shape=rake.shape),rake , zs=0, zdir='z',color='b')
ax.text(135, -210, 0,'B1', style='italic', fontsize=15,verticalalignment='center',horizontalalignment='center')
ax.text(135, 200, 0,'B2', style='italic', fontsize=15,verticalalignment='center',horizontalalignment='center')
ax.text(-100, 240, 1.4,'(a)',horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center',\
fontsize=20, color='k',alpha=1,zorder=1)
#%% 3.2. strike subplot
ax = plt.subplot(gs1[-1, 1])
x = np.linspace(0, 360, strike_num)
tt = []
yy = []
for i in range(0,Num_stem,1):
if i == 0:
tt.append(x[0])
yy.append(strike_2D[0])
else:
index = math.floor(i*strike_num/Num_stem)
tt.append( x[index] )
yy.append( strike_2D[index] )
markerline, stemlines, baseline=ax.stem(tt, yy, linefmt='grey', markerfmt='D', bottom=0)
markerline.set_markerfacecolor('none')
ax.set_xlabel('Strike')
ax.set_xlim(-5, 365)
ax.set_ylim(0.2, 1.1)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_visible(True)
ax.spines['left'].set_visible(False)
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(True)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(60)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator)
ax.set_title('A1——A2 | rake=-170°',fontsize=15)
ax.text(-5, 1.3,'(c)',horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center',\
fontsize=20, color='k',alpha=1,zorder=1)
#%% 3.3. rake subplot
ax = plt.subplot(gs1[-1, 0])
x = np.linspace(-180, 180, rake_num)
Num_stem = 40
tt = []
yy = []
for i in range(0,Num_stem,1):
if i == 0:
tt.append(x[0])
yy.append(rake_2D[0])
else:
index = math.floor(i*rake_num/Num_stem)
tt.append( x[index] )
yy.append( rake_2D[index] )
markerline, stemlines, baseline=ax.stem(tt, yy, linefmt='grey', markerfmt='D', bottom=0)
markerline.set_markerfacecolor('none')
ax.set_xlabel('Rake')
ax.set_xlim(-185, 185)
ax.set_ylim(0.2, 1.1)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_visible(True)
ax.spines['left'].set_visible(False)
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(True)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(60)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator)
ax.set_title('B1——B2 | strike=138°',fontsize=15)
ax.text(-185, 1.3,'(b)',horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center',\
fontsize=20, color='k',alpha=1,zorder=1)
#%% 4. save figure
# plt.show()
# figurename=os.path.join('./grid1.pdf')
# fig.savefig(figurename,dpi=800, format='pdf')
Text(-185, 1.3, '(b)')
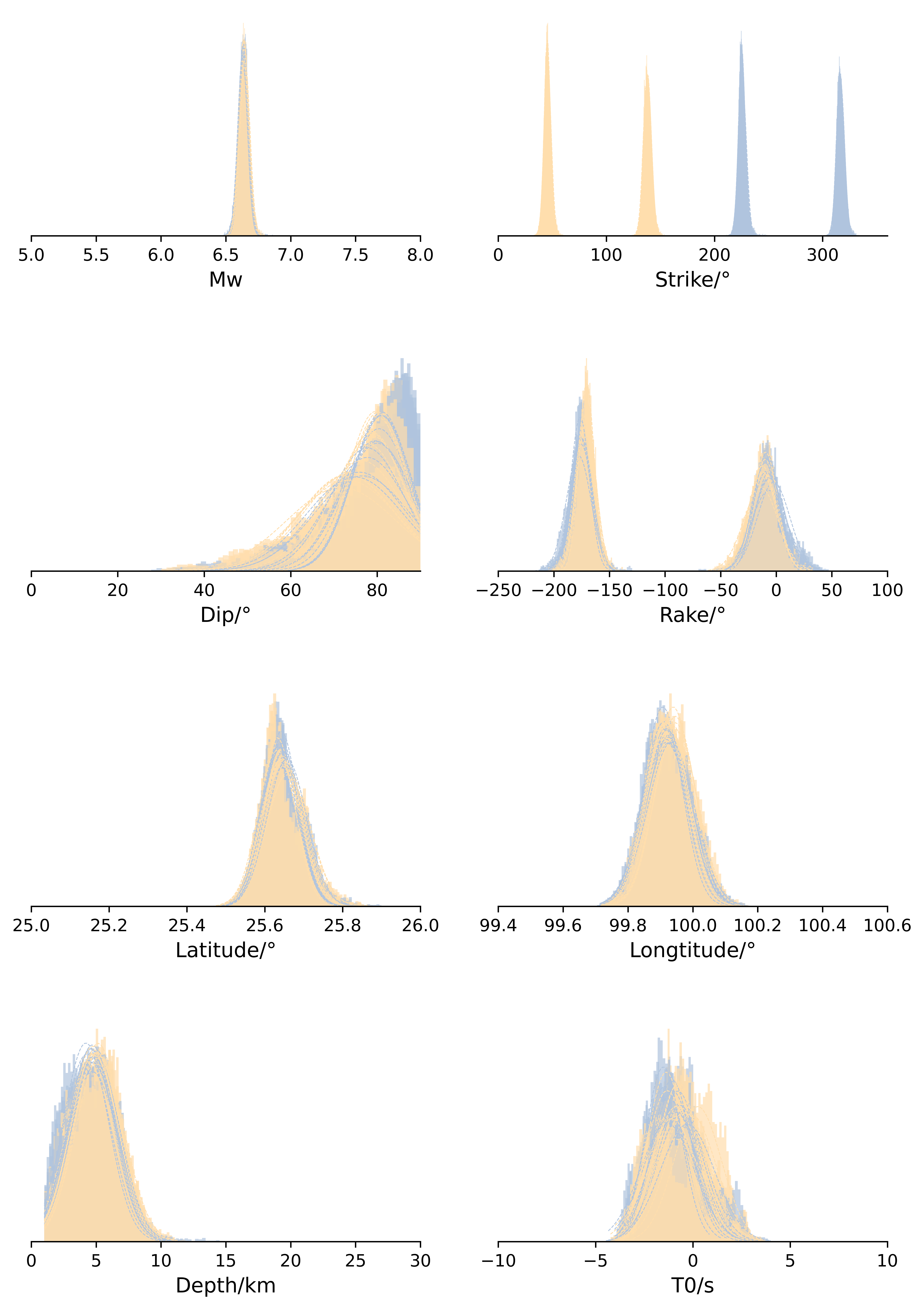
1D Histogram#
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Fri Jul 30 16:16:28 2021
@author: yf
"""
import numpy as np
import os,sys
import json5
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from obspy.imaging.beachball import beachball
#%% 1.input path
sample_path = './matplotlib_files/1d-histogram'
MPI_n=30 # 第一次试验:其中 MPI-3 与 MPI-9 采样陷入了极小值,从0开始数 || 第二次实验:MPI-24
MPI_n_st = 0
Chains_n_st = 0
num_bins=50
N = 2000 # 从第几个开始画
#%% 2.read data
FM_all=[]
for i in range(0,MPI_n,1):
if i!=4 and i!=12 and i!=15:
rank_path = os.path.join(sample_path,'Output_'+'rand_'+str(i),'rank_'+str(MPI_n_st)+'_output')
FM_path = os.path.join(rank_path,'chain_'+str(Chains_n_st)+'_FM_2_accept_all')
FM = np.loadtxt(FM_path)
FM_all.append(FM)
FM1=[];FM2=[]
LM1=[];LM2=[]
MPI_n = MPI_n-3
## 2.1 纠正 strike/rake 的周期跳跃问题
for i in range(0,MPI_n,1):
for k in range(1,4,1):
for j in range(0,FM_all[i].shape[0]):
if k==1: # strike 周期跳跃
if FM_all[i][j,k]>360 and FM_all[i][j,k]<720:
FM_all[i][j,k]=FM_all[i][j,k]-360
if FM_all[i][j,k]<0 and FM_all[i][j,k]>(-360):
FM_all[i][j,k]=FM_all[i][j,k]+360
if k==3: # rake 周期跳跃
if FM_all[i][j,k]>120:
FM_all[i][j,k]=FM_all[i][j,k]-360
## 2.2 分为4组解
for i in range(0,MPI_n,1):
strike_mean = FM_all[i][:,1].mean()
if strike_mean>100 and strike_mean<150: # FM1
FM1.append(i)
if strike_mean>0 and strike_mean<80: # FM5
FM2.append(i)
if strike_mean>300 and strike_mean<360: # LM1
LM1.append(i)
if strike_mean>200 and strike_mean<250: # LM2
LM2.append(i)
if strike_mean>250 and strike_mean<300: # LM2 # 找到未收敛的 core 每次可能不一样!!
# print(i)
pass
## 2.3 计算4组解的平均值
LM1_mu_all=[]
LM1_sigma_all=[]
for i in LM1:
mu_all=[]
sigma_all=[]
for k in range(0,8,1):
mu=np.around(np.mean(FM_all[i][N:,k]), decimals=5) # Keep two decimal places
sigma =np.around(np.std(FM_all[i][N:,k]), decimals=5)
mu_all.append(mu)
sigma_all.append(sigma)
LM1_mu_all.append(mu_all)
LM1_sigma_all.append(sigma_all)
LM1_mu=np.around(np.mean(LM1_mu_all,axis=0),decimals=2)
LM1_sigma=np.around(np.mean(LM1_sigma_all,axis=0),decimals=2)
LM2_mu_all=[]
LM2_sigma_all=[]
for i in LM2:
mu_all=[]
sigma_all=[]
for k in range(0,8,1):
mu=np.around(np.mean(FM_all[i][N:,k]), decimals=5) # Keep two decimal places
sigma =np.around(np.std(FM_all[i][N:,k]), decimals=5)
mu_all.append(mu)
sigma_all.append(sigma)
LM2_mu_all.append(mu_all)
LM2_sigma_all.append(sigma_all)
LM2_mu=np.around(np.mean(LM2_mu_all,axis=0),decimals=2)
LM2_sigma=np.around(np.mean(LM2_sigma_all,axis=0),decimals=2)
FM1_mu_all=[]
FM1_sigma_all=[]
for i in FM1:
mu_all=[]
sigma_all=[]
for k in range(0,8,1):
mu=np.around(np.mean(FM_all[i][N:,k]), decimals=5) # Keep two decimal places
sigma =np.around(np.std(FM_all[i][N:,k]), decimals=5)
mu_all.append(mu)
sigma_all.append(sigma)
FM1_mu_all.append(mu_all)
FM1_sigma_all.append(sigma_all)
FM1_mu=np.around(np.mean(FM1_mu_all,axis=0),decimals=2)
FM1_sigma=np.around(np.mean(FM1_sigma_all,axis=0),decimals=2)
FM2_mu_all=[]
FM2_sigma_all=[]
for i in FM2:
mu_all=[]
sigma_all=[]
for k in range(0,8,1):
mu=np.around(np.mean(FM_all[i][N:,k]), decimals=5) # Keep two decimal places
sigma =np.around(np.std(FM_all[i][N:,k]), decimals=5)
mu_all.append(mu)
sigma_all.append(sigma)
FM2_mu_all.append(mu_all)
FM2_sigma_all.append(sigma_all)
FM2_mu=np.around(np.mean(FM2_mu_all,axis=0),decimals=2)
FM2_sigma=np.around(np.mean(FM2_sigma_all,axis=0),decimals=2)
#%% 3. plot
fig, axs = plt.subplots(4, 2, dpi=800,figsize=(9, 13))
# plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Times New Roman']
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace =0.2, hspace =0.5)
for k in range(0,8,1):
s1 = k//2
s2 = k%2
for i in range(0,MPI_n,1):
# if i!=3 and i!=9:
if i!=24:
mu=np.around(np.mean(FM_all[i][N:,k]), decimals=5) # Keep two decimal places
sigma =np.around(np.std(FM_all[i][N:,k]), decimals=5)
if i in FM1:
facecolor = 'navajowhite'
elif i in FM2:
facecolor = 'navajowhite'
elif i in LM1:
facecolor = 'lightsteelblue'
else:
facecolor = 'lightsteelblue'
n, bins, patches = axs[s1,s2].hist(FM_all[i][N:,k], num_bins, density=True,histtype='stepfilled', facecolor=facecolor,alpha=0.7)
y = ((1 / (np.sqrt(2 * np.pi) * sigma)) *
np.exp(-0.5 * (1 / sigma * (bins - mu))**2))
axs[s1,s2].plot(bins, y, '--',color=facecolor,linewidth=0.5) # Draw a Gaussian fitting curve
if k==0:
# axs[s1,s2].text(5, max(y), str(f'FM1:{FM1_mu[0]}\nFM2:{FM2_mu[0]}\nLM1:{LM1_mu[0]}\nLM2:{LM2_mu[0]}'),
# # style='italic', fontsize=15,verticalalignment='center',
# horizontalalignment='center',bbox = dict(facecolor = "orange", alpha = 0.6))
axs[s1,s2].set_xlim(5,8)
axs[s1,s2].set_xlabel('Mw', fontsize=12)
if k==1:
axs[s1,s2].set_xlim(0,360)
axs[s1,s2].set_xlabel('Strike/°', fontsize=12)
if k==2:
axs[s1,s2].set_xlim(0,90)
axs[s1,s2].set_xlabel('Dip/°', fontsize=12)
if k==3:
axs[s1,s2].set_xlim(-250,100)
axs[s1,s2].set_xlabel('Rake/°', fontsize=12)
if k==4:
axs[s1,s2].set_xlim(25,26)
axs[s1,s2].set_xlabel('Latitude/°', fontsize=12)
if k==5:
axs[s1,s2].set_xlim(99.4,100.6)
axs[s1,s2].set_xlabel('Longtitude/°', fontsize=12)
if k==6:
axs[s1,s2].set_xlim(0,30)
axs[s1,s2].set_xlabel('Depth/km', fontsize=12)
if k==7:
axs[s1,s2].set_xlim(-10,10)
axs[s1,s2].set_xlabel('T0/s', fontsize=12)
axs[s1,s2].spines['bottom'].set_visible(True)
axs[s1,s2].spines['top'].set_visible(False) # Coordinate boxes are not displayed
axs[s1,s2].spines['right'].set_visible(False)
axs[s1,s2].spines['left'].set_visible(False)
axs[s1,s2].get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
# fig.savefig('./pdf/randFM.pdf', dpi=800, format='pdf')
#%% 4. beachball
# fig = beachball(FM1_mu[1:4], size=200, linewidth=1, facecolor='g')
# fig.savefig('./pdf/FM1.pdf', dpi=800, format='pdf')
# fig = beachball(FM2_mu[1:4], size=200, linewidth=1, facecolor='g')
# fig.savefig('./pdf/FM2.pdf', dpi=800, format='pdf')
# fig = beachball(LM1_mu[1:4], size=200, linewidth=1, facecolor='g')
# fig.savefig('./pdf/LM1.pdf', dpi=800, format='pdf')
# fig = beachball(LM2_mu[1:4], size=200, linewidth=1, facecolor='g')
# fig.savefig('./pdf/LM2.pdf', dpi=800, format='pdf')
#%% 5. save
# fp = open(os.path.join('./pdf/FM_mu_sigma.txt'), 'w')
# for m in range(0,len(FM1_mu)):
# fp.write(str(FM1_mu[m]))
# fp.write('\t')
# fp.write(str(FM1_sigma[m]))
# fp.write('\t')
# fp.write('\n')
# for m in range(0,len(FM2_mu)):
# fp.write(str(FM2_mu[m]))
# fp.write('\t')
# fp.write(str(FM2_sigma[m]))
# fp.write('\t')
# fp.write('\n')
# for m in range(0,len(LM1_mu)):
# fp.write(str(LM1_mu[m]))
# fp.write('\t')
# fp.write(str(LM1_sigma[m]))
# fp.write('\t')
# fp.write('\n')
# for m in range(0,len(LM2_mu)):
# fp.write(str(LM2_mu[m]))
# fp.write('\t')
# fp.write(str(LM2_sigma[m]))
# fp.write('\t')
# fp.write('\n')
# fp.close()
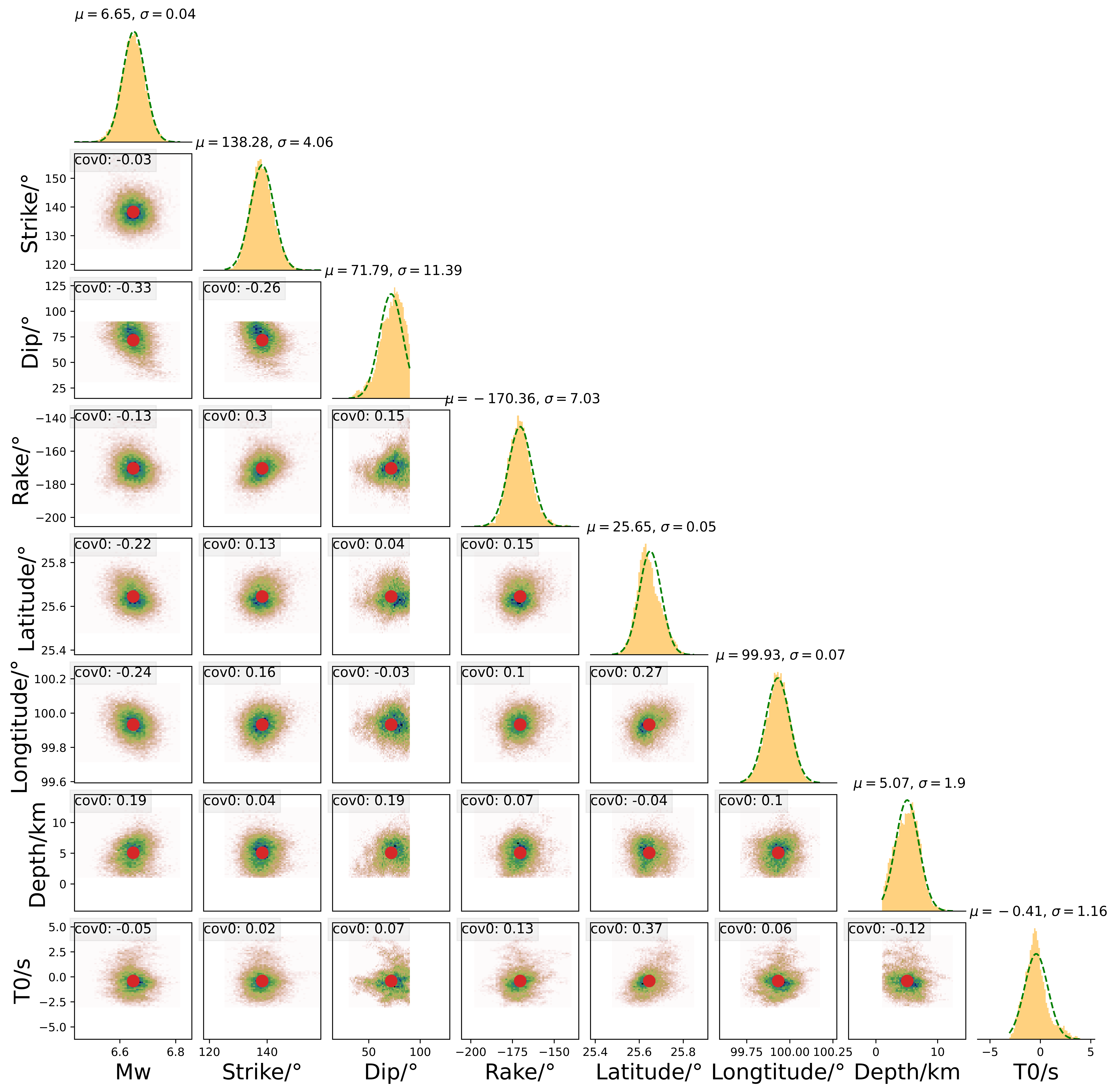
2D Histogram#
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Mar 21 00:20:35 2021
@author: Fu Yin (yinfu@mail.ustc.edu.cn) at USTC
This script:
1) plot hist
Modify history:
1) Mar 21 00:20:35 2021 || Fu Yin at USTC || The initial release.
2) Jun 28 11:08:02 2021 || Fu Yin at USTC || Add figure format parameter.
"""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import os
import sys
from math import sqrt
##############################################################################
def plot_hist(FM_all,FM_accept_all,num_bins,num_std,labels_name,Fixed_FM,InvType,fig_format):
FM = FM_all
figurename=os.path.join('hist.'+fig_format)
if InvType == 'mt':
N_all = 11
elif InvType == 'dc':
N_all = 8
elif InvType == 'sf':
N_all = 8
elif InvType == 'mt':
N_all = 5
N = Fixed_FM.count('variable') # plot: The number of subgraphs of a row
delete_list=[]
for i in range(0,N_all,1):
if Fixed_FM[i]!='variable':
delete_list.append(i)
FM = np.delete(FM,delete_list, axis=1) # The delete solution that is a fixed parameter
FM_mean=np.zeros(shape=(N))
FM_sigma=np.zeros(shape=(N))
for i in range(0,N,1):
FM_mean[i]=np.mean(FM[0:,i]) # FM The mean of each parameter
FM_sigma[i]=np.std(FM[0:,i]) # FM The standard deviation of each parameter
FM_used = FM.copy() # strike rake cycle skip
if InvType=='dc':
if FM_mean[1]>360 and FM_mean[1]<720:
FM_used[:,1]=FM_used[:,1]-360
FM_mean[1]=FM_mean[1]-360
if FM_mean[1]<0 and FM_mean[1]>(-360):
FM_used[:,1]=FM_used[:,1]+360
FM_mean[1]=FM_mean[1]+360
if FM_mean[3]>180 and FM_mean[3]<540:
FM_used[:,3]=FM_used[:,3]-360
FM_mean[3]=FM_mean[3]-360
if FM_mean[3]<(-180) and FM_mean[3]>(-540):
FM_used[:,3]=FM_used[:,3]+360
FM_mean[3]=FM_mean[3]+360
plt.style.use('default') # Use the default plotting style (make sure it's not the ggplot style)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(N, N, dpi=800,figsize=(16, 16))
# plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Times New Roman']
for i in range(0,N,1):
for j in range(0,N,1):
x=FM_used[:,i]
y=FM_used[:,j]
axs[i,j].get_xaxis().set_visible(False) # Do not display the axes
axs[i,j].get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
if j==0:
axs[i,j].get_yaxis().set_visible(True)
axs[i,j].set_ylabel(labels_name[i],fontsize=19) # The left axis labels
if i==N-1:
axs[i,j].get_xaxis().set_visible(True)
axs[i,j].set_xlabel(labels_name[j],fontsize=19) # The bottom axis labels
if i<j:
axs[i,j].set_axis_off() # The upper right part of the image is not displayed
if i>j:
h, xx, yy, p=axs[i,j].hist2d( y,x, bins=(50, 50), cmap=plt.cm.gist_earth_r) # hist2d
x_start = FM_mean[j]-num_std*FM_sigma[j] # Adjust the range of the coordinate axes
x_end = FM_mean[j]+num_std*FM_sigma[j]
y_start = FM_mean[i]-num_std*FM_sigma[i]
y_end = FM_mean[i]+num_std*FM_sigma[i]
axs[i, j].set_xlim(x_start,x_end)
axs[i, j].set_ylim(y_start,y_end)
axs[i,j].scatter(FM_mean[j],FM_mean[i],s=100,c='tab:red') # Draw the average value (red dots)
# plt.clf()
# axs[i,j].imshow(h, origin = "lower", interpolation = "gaussian",cmap=plt.cm.gist_earth_r)
cov_yx = np.cov(y.T, x.T) # Covariance matrix
cov0_yx = np.around(cov_yx[0,1]/sqrt(cov_yx[0,0]*cov_yx[1,1]), decimals=2) # The correlation coefficient
cov0_yx_text = 'cov0: '+str(cov0_yx)
axs[i,j].text(x_start, y_end,cov0_yx_text,horizontalalignment='left', verticalalignment='top',
fontsize=12, color='black',bbox = dict(facecolor = "k", alpha = 0.05)) # Mark the correlation coefficient SHIFT
if i==j:
axs[i,j].spines['top'].set_visible(False) # Coordinate boxes are not displayed
axs[i,j].spines['right'].set_visible(False)
axs[i,j].spines['left'].set_visible(False)
axs[i,j].spines['bottom'].set_visible(False)
axs[i,j].get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
n, bins, patches = axs[i,j].hist(x, num_bins, density=True,histtype='stepfilled', facecolor='orange',
alpha=0.5) # histgram
mu=np.around(FM_mean[i], decimals=2) # Keep two decimal places
sigma =np.around(FM_sigma[i], decimals=2)
y = ((1 / (np.sqrt(2 * np.pi) * sigma)) *
np.exp(-0.5 * (1 / sigma * (bins - mu))**2))
axs[i,j].plot(bins, y, '--',color='g') # Draw a Gaussian fitting curve
str_hist=' $\mu='+str(mu)+'$, $\sigma='+str(sigma)+'$'
axs[i,j].set_title(r' $\mu='+str(mu)+'$, $\sigma='+str(sigma)+'$')
x_start = FM_mean[j]-num_std*FM_sigma[j] # Adjust the range of the coordinate axes
x_end = FM_mean[j]+num_std*FM_sigma[j]
y_start = FM_mean[i]-num_std*FM_sigma[i]
y_end = FM_mean[i]+num_std*FM_sigma[i]
axs[i,j].set_xlim(x_start,x_end)
axs[i,j].spines['bottom'].set_visible(True) # Shows the axis of coordinates at the bottom
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace =0.1, hspace =0.1)
# fig.savefig(figurename,dpi=800, format=fig_format)
##############################################################################
sample_path = './matplotlib_files/2d-histogram/'
fig_format = 'pdf' # history: Jun 28 11:08:02 2021
MPI_n = 1
Chains_n = 1
num_bins = 50 # plot hist2d: the number of grid
num_std = 5 # range of axes in each subgraph (mean +- several times standard deviation)
labels_name = ['Mw','Strike/°','Dip/°','Rake/°','Latitude/°','Longtitude/°','Depth/km','T0/s'] # labels:['mw','strike/°','dip/°','rake/°','x/km','y/km','z/km','t0/s']
N_start = 0
N_start_accept = 0
Fixed_FM = ['variable','variable','variable','variable', 'variable','variable','variable','variable',]
InvType = 'dc' # 'mt' 'dc' 'sf' 'ep'
N_k = 2000
for i in range(0,MPI_n,1):
rank_path = os.path.join(sample_path,'rank_'+str(i)+'_output')
for j in range(0,Chains_n,1):
FM_2_all_path = os.path.join(rank_path,'chain_'+str(j)+'_FM_2_all')
FM_2_accept_path = os.path.join(rank_path,'chain_'+str(j)+'_FM_2_accept_all')
if i==0 and j==0:
FM_2_all = np.loadtxt(FM_2_all_path)[N_start:,:]
FM_2_accept_all = np.loadtxt(FM_2_accept_path)[N_start_accept:,:]
else:
FM_2_all = np.vstack( ( FM_2_all, np.loadtxt(FM_2_all_path)[N_start:,:] ) )
FM_2_accept_all = np.vstack( ( FM_2_accept_all, np.loadtxt(FM_2_accept_path)[N_start_accept:,:] ) )
plot_hist(FM_2_all,FM_2_accept_all,num_bins,num_std,labels_name,Fixed_FM,InvType,fig_format)