Introduction
Contents
Introduction#
Author: Fu Yin
Update: Dec 26, 2022
Reading: 120 min
Preliminary Knowledge#
What is the cores in CPU?#
The concepts of the node, physical cores, computing cores, and Hyper-Threading Technology:
For clusters, a cluster has multiple node nodes, each node can have multiple CPUs (
physical cores), each CPU can have multiple cpu cores (computing cores), and each core can run two threads which is calledHyper-Threading Technology.One process can have many threads, after CPU dispatched, those threads can run in different
computing cores.Because a thread belongs to a process, a single process can only run under a single node, so threads cannot share memory across nodes. As for the physical core, the laptop we buy has a cpu chip, which is a single
physical core, but this chip may have 4 cores, and there are 4computing cores.
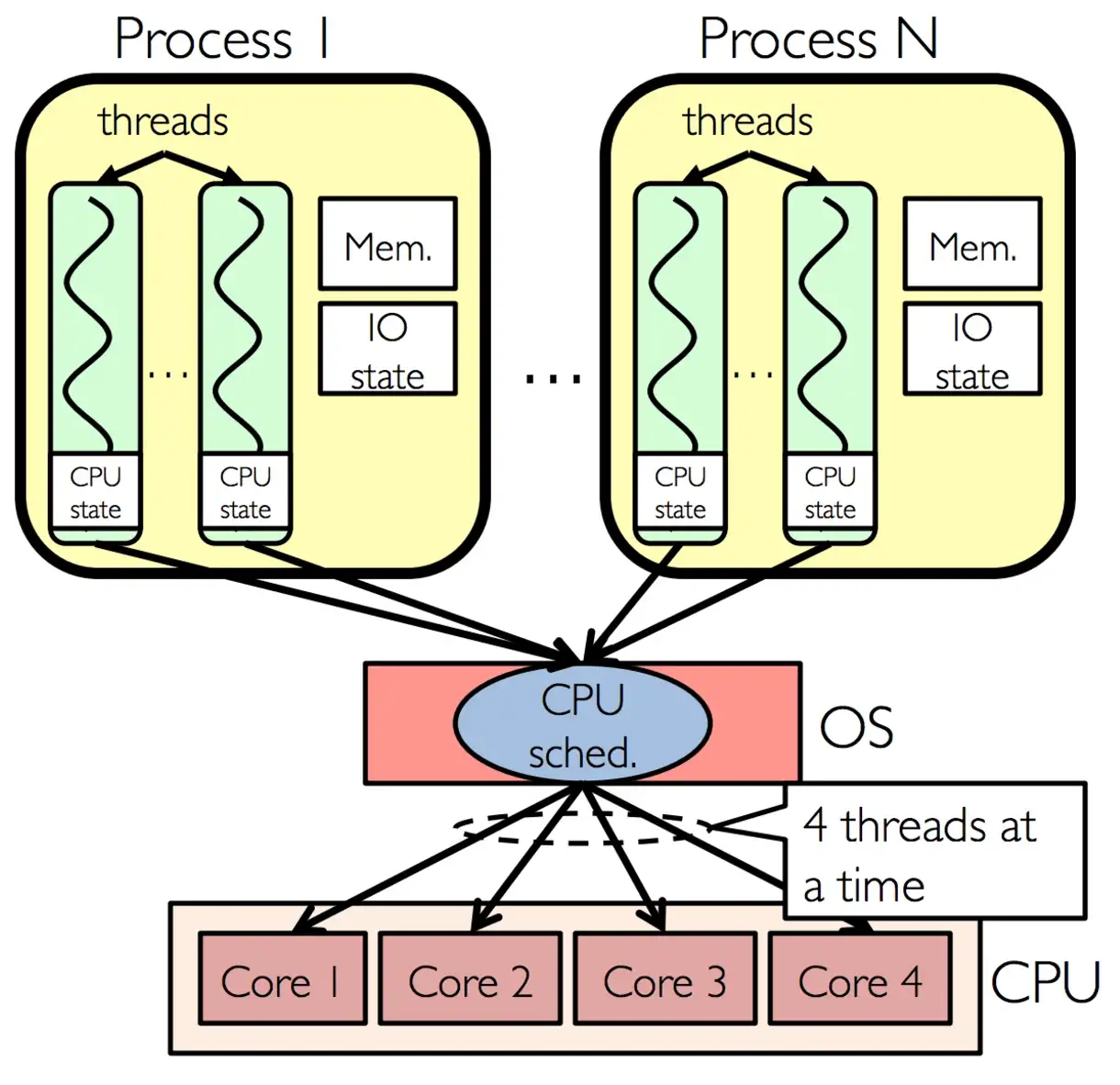
Fig. 15 Single Threading Technology#
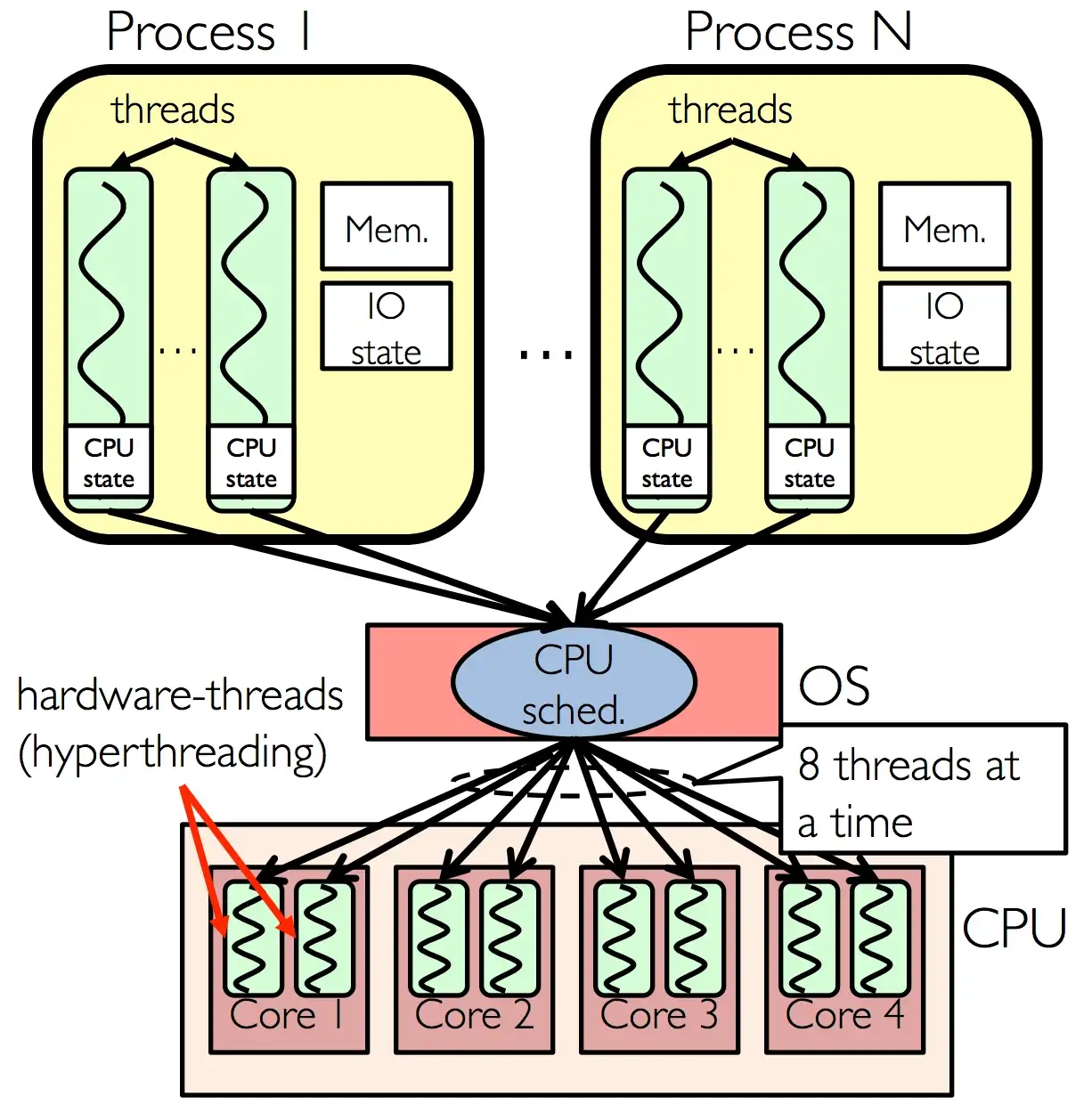
Fig. 16 Hyper Threading Technology#
How the CPU works?#
The concept of thread, process, Round-robin scheduling, CPU-bound, I/O bound, disk read speed and bandwidth, where is the time spent for a task? How many threads and processes we use are appropriate?
Round-robin (RR) scheduling is one of the algorithms employed by process and network schedulers in computing. As the term is generally used, time slices (also known as time quanta) are assigned to each process or thread in equal portions and in circular order, handling all processes without priority (also known as cyclic executive).

Fig. 17 Round Robin Schedule Example from Wikipedia#
One process can generate many thread missions, and a process is cheap than a thread. Why? When a process is suspended, it needs to record the state at this time. When a process resumes, it needs to collect the state of the previous moment and then execute the program. We call this working time is context switching time.
Thread is the smallest scheduling unit. Process is the smallest unit of operating system resource allocation (memory, graphics card, disk), and a thread is the smallest unit of execution scheduling (that is, cpu scheduling) (cpu sees threads instead of processes). A process can have one or more Threads share process resources between threads. Through this paradigm, the cost of creating and destroying processes can be reduced, the number of processes can be reduced, and the process can be kept relatively stable. So just keep scheduling threads.
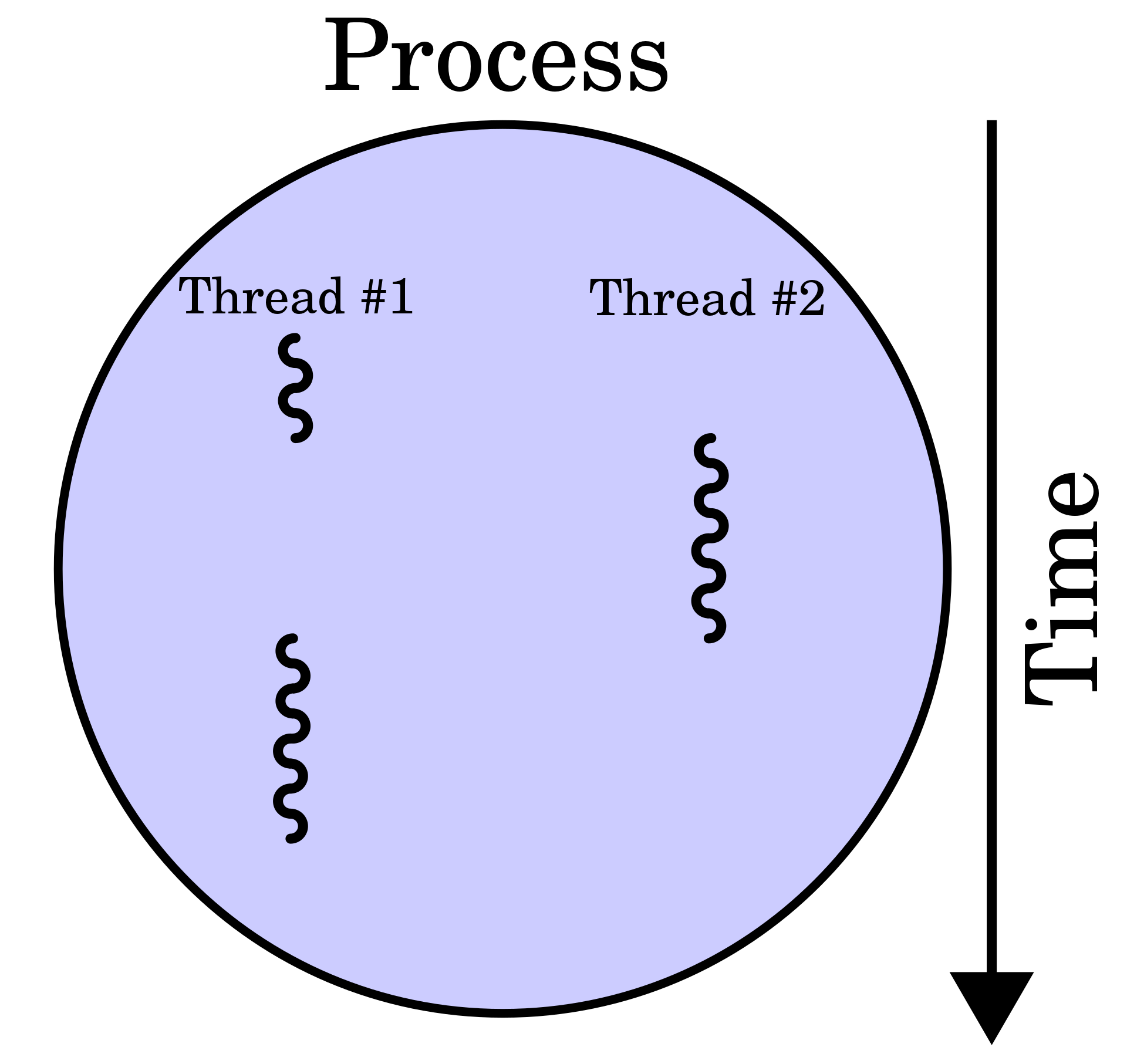
Fig. 18 A schematic diagram process and thread#
Question: where is the time spent for a task?
For a task, not only
cpu computingtakes the time, butNetwork I/OandDisk I/Oalso take the time.When you send a task (read data) to system, the system will order disk to read data into memory,
Disk I/Ois dependent on HDD speed (disk read speed).When you send a task to download data in Internet, you need to gain data via network,
Network I/Ois dependent onbandwidth. Imagine there are 10 lanes on a road, and a car runs on each lane. (a lane is a thread)cpu computingmainly includes using memory to compute some data.
Question: due to the Round-robin scheduling, a CPU core will only execute one process at same time. So how many threads and processes we use are appropriate?
CPU-bound:computing cores + 1, orcomputing cores * 2. I’d like personally to use computing cores + 1 choice.Network I/O: it depends, the empirical formula iscomputing cores / 0.1, for example in a network IO task, the whole process issend requestion via CPU–>send back data via network (network IO)–>parse requestion vis cpu. But after you send the request via CPU, your CPU is free, and the work is to wait network to send back data, so the utilization rate of CPU is not high at this time.If you use
a processto do this task, you must need to wait network IO time, and after that you can run next step code.If you use
multi-threadsto do this task, when you wait the response of network, you can run other threads to send requests, and thus enhance the utilization rate of CPU.If you use
multi-processesto do this task, if will also save much time as same asmulti-threadsapproach. But creating many processes is more expensive (in memory and time aspects) than creating multi threads. Why? At this time, the working time of multiple processes is spent oncontext switching, because the CPU has time slicing and runs different processes at different times. So multi-process will use more time then multi-thread.The limitation is
bandwidth(network transmission speed, e.g. 100 MB/s), because the bandwidth is a constant number, it is useless to use more threads.
Disk bound (small data files): same as network I/O, for example, you need to read many data files to do computing, the whole process issend read data mission via CPU–>IO system reads data into memory–>do computing task. When you read many small files, thedisk read speedandbandwidthis not the limitation factor, and the main time is spent on other operations such as finding the address of the small file (seek time). So when IO system reads data into memory, your CPU is free at this time, you can usemulti-threadsto enhance the efficiency.Disk bound (big data files): single thread or process is well. Under this circumstance, the limitation is thedisk read speedandbandwidth, and the multi-threads reading will not significantly increase the speed.
What is the Parallel Computing?#
Parallel Computing is the general name Cluster Computing, Distributed Computing, and Cloud Computing.
Cluster Computing#
Cluster Computing: cluster computing is a single-task, high-efficiency computing group, and there are fast communication lines between different nodes, and the most common cluster isHigh-performance clusters (HPC)
The main three ways for HPC computing:
OpenMPthe full name is open multi-processing, supportc,c++, andfortranlanguage,gccandclangof compilers. Shared memory (all threads can access all variables, just call the variable name), belongs to the one process, and cannot work on multiple nodes in the cluster (distributed memory), but work only on a single node. As long as multiple threads do not write at the same time, it is safe, and if you want to write, you need to uselockfunction.OpenMPIthe full name is open message passing interface. Each processes has independent memory, and different processes can communicate (with performance memory overhead), suitable for various tasks such as large clusters with multiple nodes.CUDAthe full name is compute unified device architecture. GPU has many many threads for computing, and we need to writekernel functionto run code in those threads. GPU computing is not independent, usually the data is send to GPU via CPU, and this process is calledheterogeneous computing.
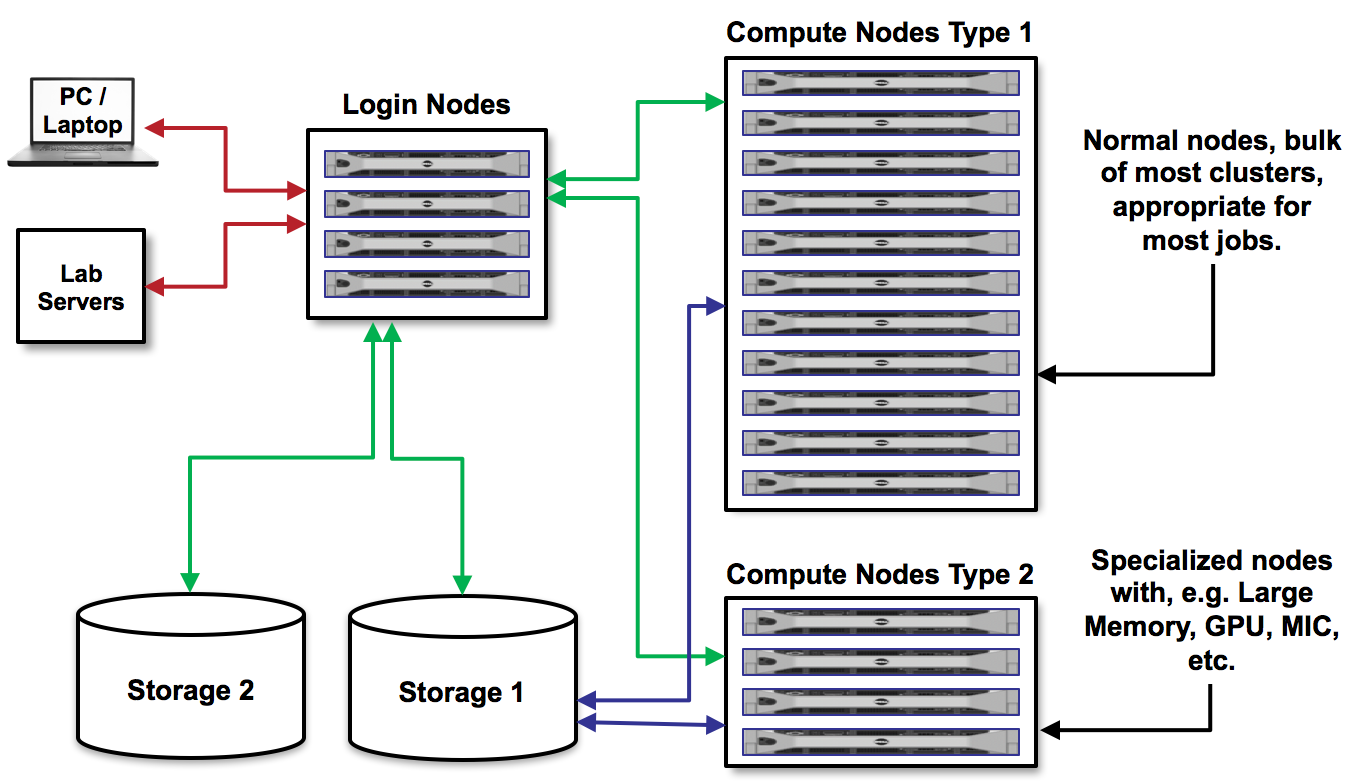
Fig. 19 A schematic diagram HPC computing#
Which one is more suitable for parallel computing, OpenMP and OpenMPI?
CPU-bound, utilizes multiple processes, and takes full advantage of multiple CPUs. Maybe, you will have doubts, since multi-threading can be executed in parallel, isn’t it also suitable for computing-intensive tasks?
In theory,
multi-processis more suitable. It means that when the amount of data is relatively large and there is no logical dependence between computing tasks, multi-process is more suitable. Because each process will have its own process memory space, each process is naturally isolated.While
multiple threadsshare the same memory space, synchronization between threads must be considered. None of these problems are necessary for computationally intensive tasks (CPU-bound). So we say that computing-intensive tasks are more suitable for multi-processing.
What is the openmpi+openmp hybrid mode?
For large-scale operations of cluster jobs:
openmpi+openmp hybrid. Usually,MPIis used for communication betweennodes, andOpenMPis used for calculation within asingle node. The communication speed within the node is fast, and is slow between nodes.For example, in the seismic forward simulation in the petroleum industry, N nodes are opened at the same time, each node is forwarded with one shot, and each shot uses several CPUs for calculation.
Distributed Computing#
Distributed Computing: it can be that many ordinary home computers are connected through traditional network cables. The transmission and communication speed of different computing points is very slow, and the tasks performed are very fragmented. Compared with cluster computingshare memory or message for communication, distributed computing communicatevia network. (e.g.spark,hadoop)For example: by installing Raspberry Pi (for computing) and Bluetooth wireless (for data transmission) on many node seismographs, the node seismographs will have the simple calculation function (such as earthquake detection, cross-correlation calculation, etc.) and the data transfer function, which can also be called distributed computing.
Storage and Distributed Storage
Ordinary Storage, such as the hard disk on the server, is connected to the server through aSAS cable(ultra-fast transmission speed, such as 10G/s). At this time, the read and write speed of the server is affected by thedisk IO speed, and the general disk speed is only 1G/s, but a server will be connected to multiple disks, as long as the transmission speed of multiple disks does not exceed 10G/s of the SAS line, reading and writing missions will not be affected.It can be seen from the above that the traditional hard disk storage method has defects. The speed of reading data is very slow, and the total
bandwidthis constant. If many people read data at the same time, and the speed will slow down seriously; and if readinga large file, it can only beread serially.Distributed Storageis to divide a piece of data into many small pieces, and store them in multiple disks respectively. When reading a big file data, it will read a lot of small pieces from multiple disks at the same time, and finally stitch them into one big piece, similar to parallel reading. It means that the speed will be very fast; but the disadvantage is that if one hard disk is broken, all distributed storage data will be broken; but the latestdistributed array storagetechnology can solve this problem.
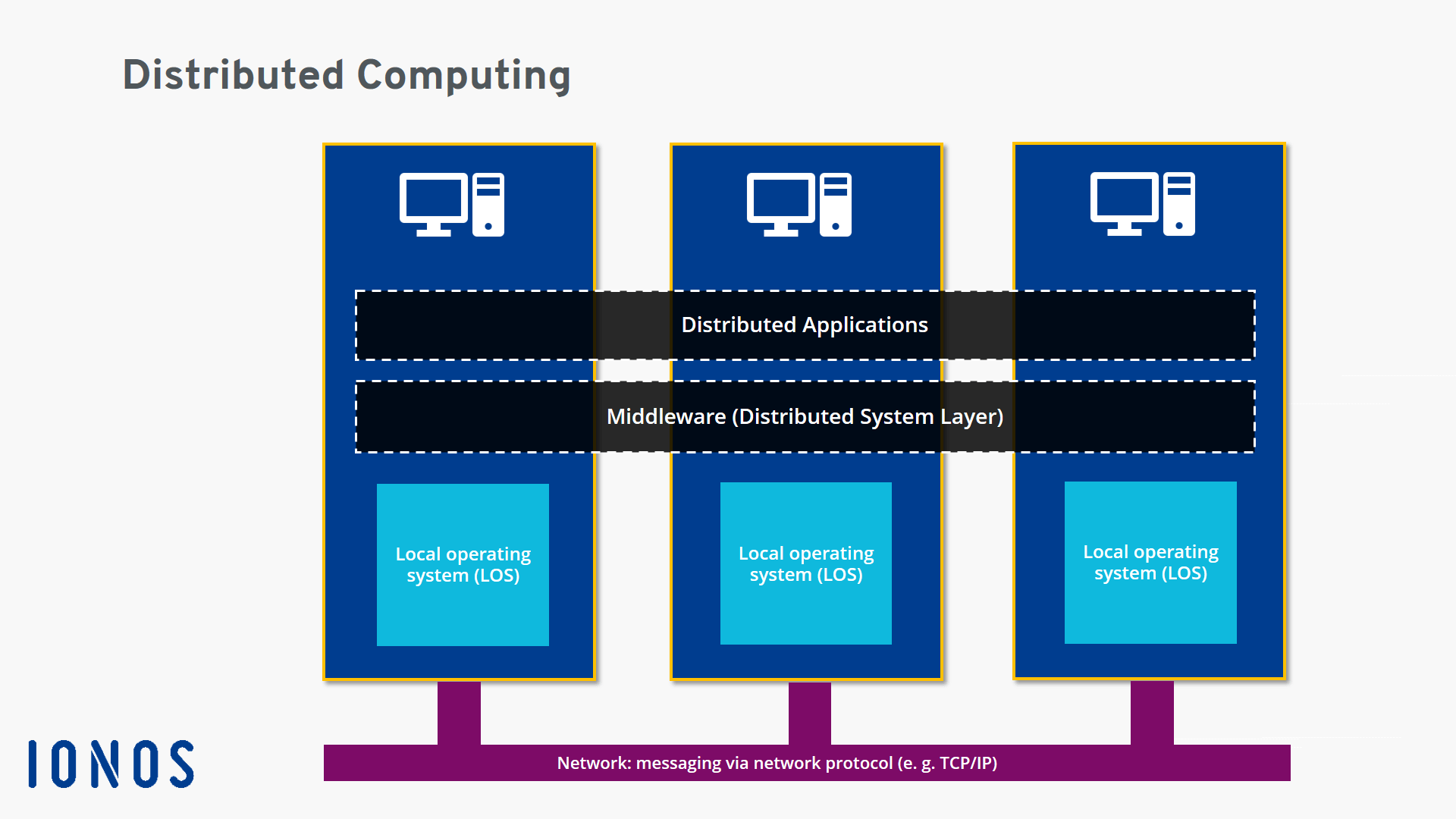
Fig. 20 A schematic diagram distributed computing#
Cloud Computing#
Cloud Computing: cloud computing is a combination of the cluster computing and the distributed computing.There is a metaphor:
Cluster Computing(supercomputing) is like centralized ticket collection at railway station counters.Distributed Computingis like scattered self-service ticket collection at railway stations.Cloud Computing(e.g. Amazon, Micrsoft, and Google cloud service) is like all ticket collection windows at railway stations.
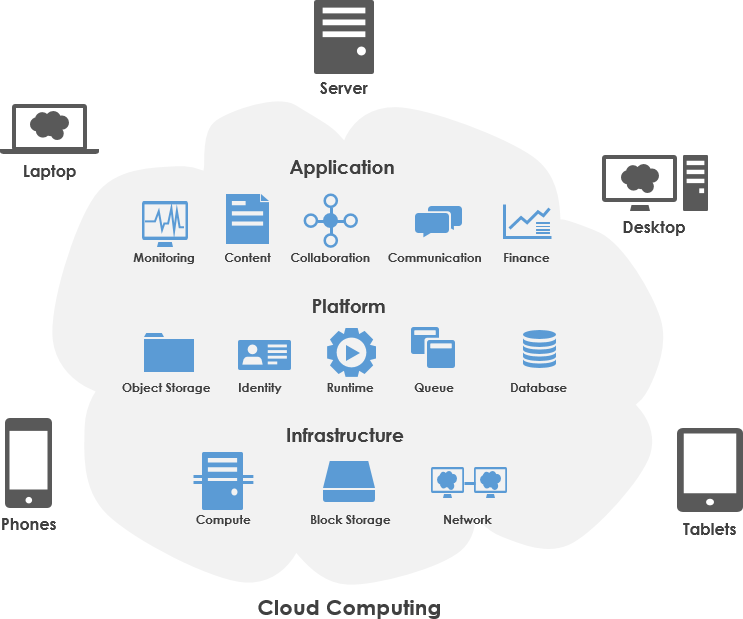
Fig. 21 A schematic diagram cloud computing#
