Shell Manual
Contents
Shell Manual#
Author: Fu Yin
Update: Dec 15, 2022
Reading: 10 min
ln#
# Print all links
ls -al
# Create a link, file2 is the link of file1.
ln -s file1 file2
scp#
scp
rsync#
rsync
conda/mamba#
# check all packages
conda list
# install package
conda install -c conda-forge xxx
# create new env
conda create -n envname python=3.9 numpy pandas
# activate env
conda activate pygmt
# deactivate env
conda deactivate
# env list
conda env list
# remove a env
conda env remove -n yourEnv
ssh/sshfs#
# ssh -p port -X user@hostname
ssh -p 22 -X fy21@nots.rice.edu
ssh nots
# sshfs NOTS HPC in Rice
sshfs -o follow_symlinks fy21@nots.rice.edu:/ /Users/yinfu/share1/
# set alias before in '~/.zshrc'
alias sshfs-nots='sshfs -o follow_symlinks -p 22 fy21@nots.rice.edu:/ /Users/yinfu/share1/'
alias resshfs-nots='diskutil umountDisk /Users/yinfu/share1; sshfs-nots'
sshfs-nots
resshfs-nots
mount/umount#
Use diskutil on MacOS, mount/umount on Linux.
Disk softwares on Mac, such as Disk Utility, Tuxera…
# List the partitions of a disk
diskutil list
# mount a single volume
diskutil mount [IDENTIFIER]
diskutil mountDisk disk2s1
# mount an entire disk
diskutil mountDisk [IDENTIFIER]/[PATH]
diskutil mountDisk disk2s1
diskutil mountDisk /dev/disk2
# umount a single volume
diskutil umount [IDENTIFIER]
diskutil umount disk2s1
# umount an entire disk
diskutil umountDisk [IDENTIFIER]/[PATH]
diskutil umountDisk disk2s1
diskutil umountDisk /dev/disk2
# umount sshfs
diskutil umountDisk [PATH]
diskutil umountDisk /Users/yinfu/share1
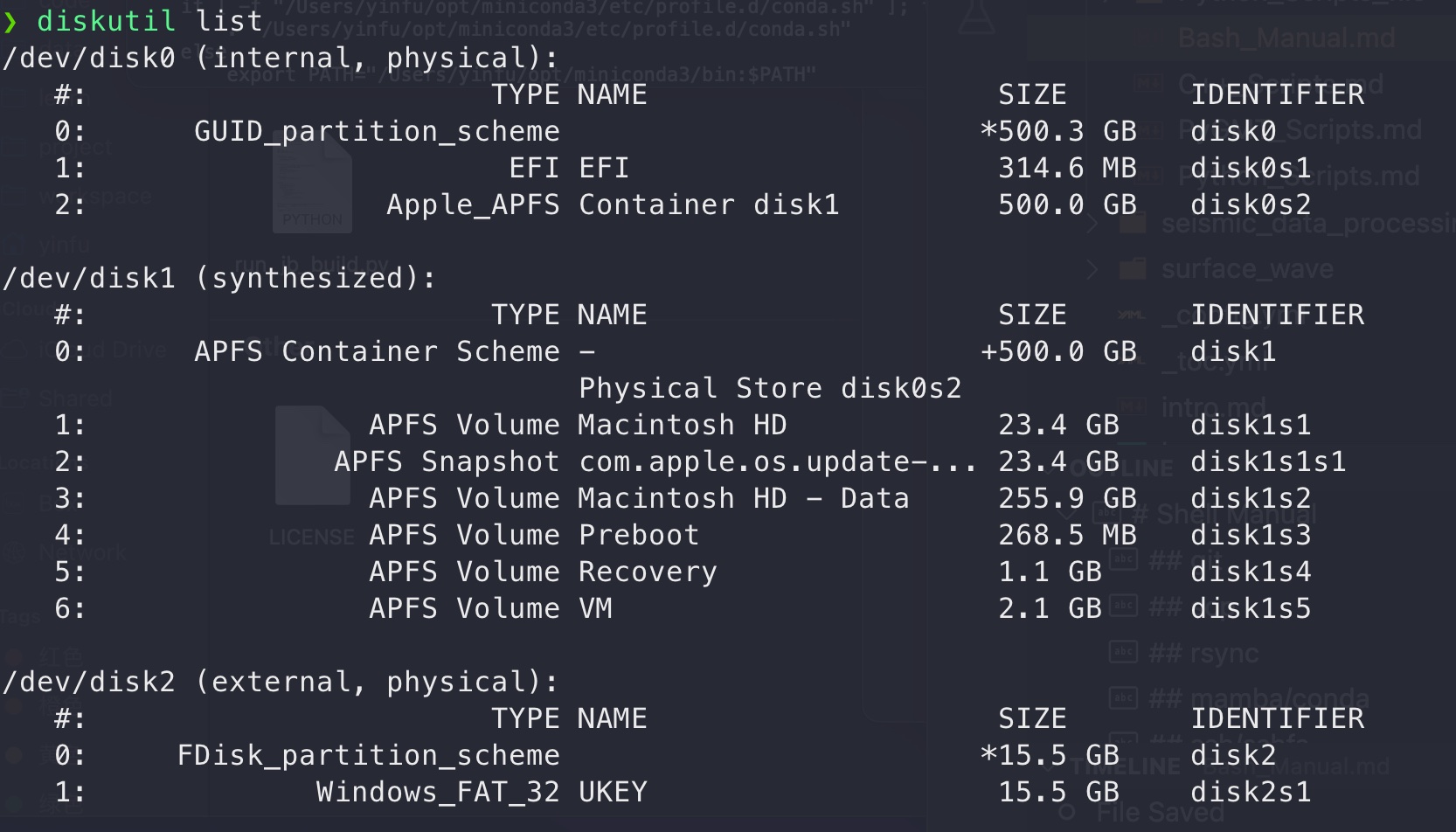
Fig. 8 My diskutil list#
df#
df full name is disk free.
# The space size of each currently mounted directory
df -h
# -ll: display bytes || -lh: display KB/MB/G/T...
ls -ll
ls -lh
# Display total file size in current directory
du -sh
# View the size of each file and folder in the current directory
du -h --max-depth=1
du -h --max-depth=1*
cat#
cat
wc#
wc full name is word count
# Find the lines, words, bytes, filenames of the file
wc file
# Find the lines of the file
cat file | wc -l
head/tail#
head
tail
top#
top
#quit
q
kill#
ps -ef | grep yinfu | awk '{ print $2 }' | xargs kill -9
nohup#
# start
nohup command > command.log 2>&1& echo $! > command.pid
# kill
kill `cat command.pid`
