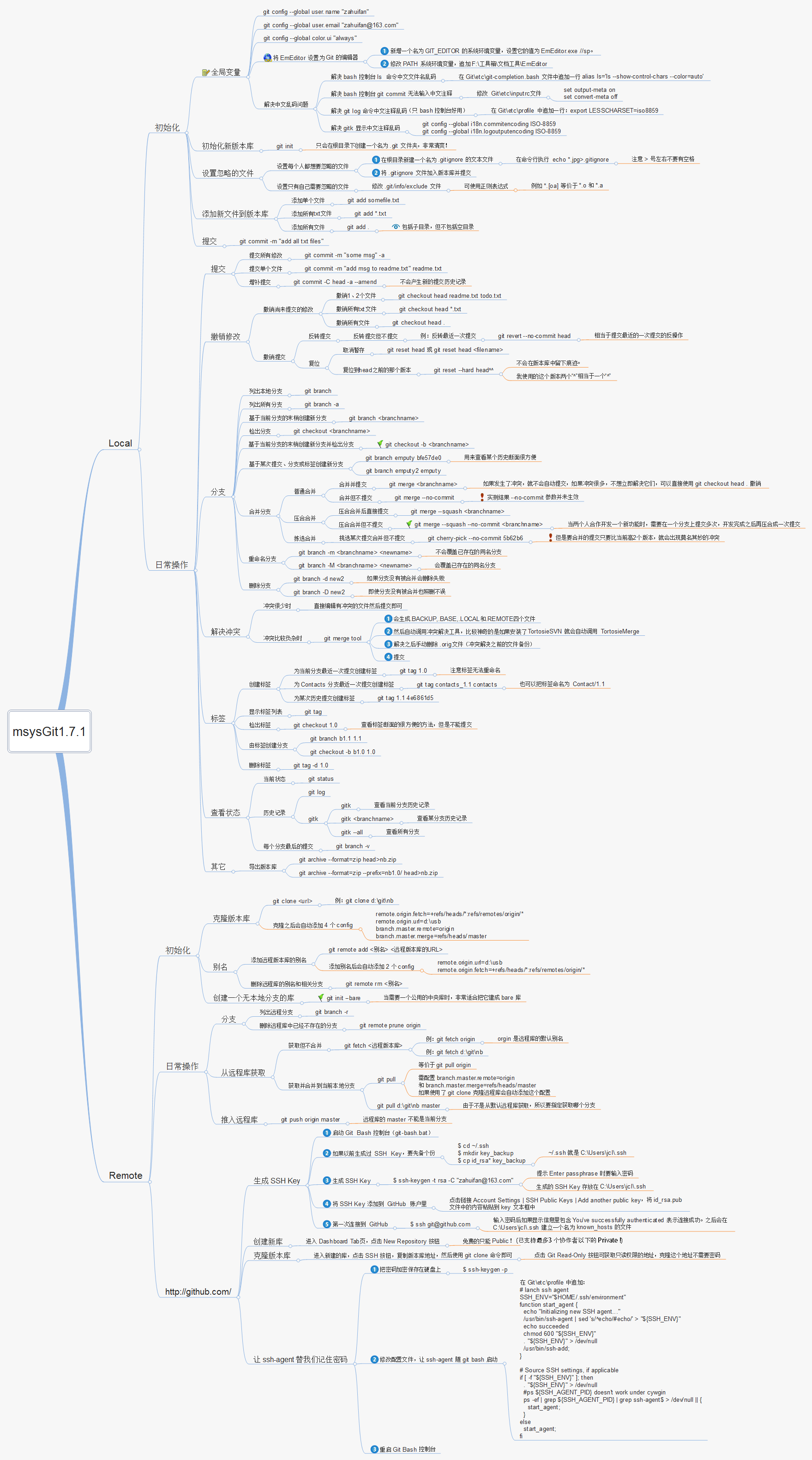
Git & Github
Contents
Git & Github#
Author: Fu Yin
Update: July 27, 2022
Reading: 60 min
Introduction#
Do you know git history?
Linus created open source system Linux in 1991. In 2005, Linus spent two weeks writing a distributed version control system in C language to manage the Linux system’s source code. Github was founded in April 2008 by Chris Wanstrath, PJ Hyett, and Tom Preston-Werner to host versions based on Git.
And now, paying users can build private repositories, free users can only use public repositories (or private repositories with up to 3 developers).
Git consists of three parts: Working Directory(工作区), Index(暂存区) and Repository(版本库):
Working Directory: the directory that you can see on your computerIndex: also called theStage, it is usually stored in the.git/indexfile.Repository: the workspace has a hidden directory, the.git, which is the repository. It usually consists of abranchandHead, with theHeadpointing to the result of your last submission.
GitHub is the single largest host for Git repositories, and we can host Git repositories on GitHub. The interaction between Git and Github is showing in figure below:
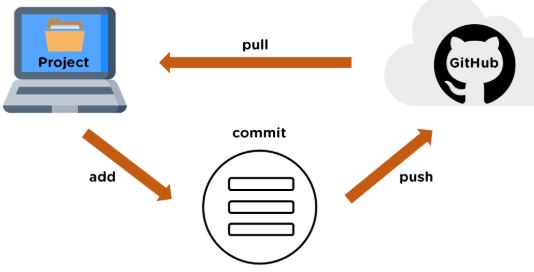
Fig. 3 Project and Github#
Install#
MacOS uses Xcode’s Command Line Tools to install Git in /usr/bin/git directory. However, Xcode usually comes with a lower version of Git, so you need brew to upgrade. After installation, remember to add the environment variable.
# install
brew install git
# add path
vim ~/.zshrc
> export GIT=/usr/local/Cellar/git/2.37.1
> export PATH=$GIT/bin:$PATH
source ~/.zshrc
# check version
git --version
After the successful installation , we need to configure git.
Do you know the meaning of git config –global ?
The Git configuration file for each repository is stored in .git/config file in each repository. But the current user’s Git configuration file is stored in ~/.gitconfig file. When configuring Git, add --global to apply to the current user, and if not, it applies only to the current repository.
username and email
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email "email@example.com"
color ui and git log
# let Git show different colors
git config --global color.ui true
# configure log command --> git lg
git config --global alias.lg "log --color --graph --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset' --abbrev-commit"
master to main
Manually modify the
~/.gitconfigfile and setdefaultBranch = main. Or use thegit configcommand for git version > v2.28:
git config --global init.defaultBranch main
Why change master to main ?
After 2020-10-01, the default branch of the GitHub repository will change to main (a neutral word) instead of master (because master is associated with master hierarchy and slavery), but will not affect all existing repositories.
But notice that Git’s default branch is still the master. So be careful to keep the default branch names the same. It is recommended to change the local Git’s default branch from master to main.
It is not recommended to change the default branch name for past projects. If you want to change the default branch name, you can rename it under the master default branch:
# With the '-m' option, you can change the branch name without affecting the git commit history from master to main.
git branch -m master main
# the above changes are only local and need to be synchronized to the remote.
git push -u origin main
My complete ~/.gitconfig file showing below:
[user]
name = OUCyf
email = oucyinfu@gmail.com
[color]
ui = true
[alias]
lg = log --color --graph --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset' --abbrev-commit
[init]
defaultBranch = main
SSH keys for Github#
Imagine the scenario that you have a remote repository on GitHub, and one computer at home and one computer at the office all be needed to submit codes using SSH keys, and both the SSH public keys are needed to be stored in the GitHub Setting.
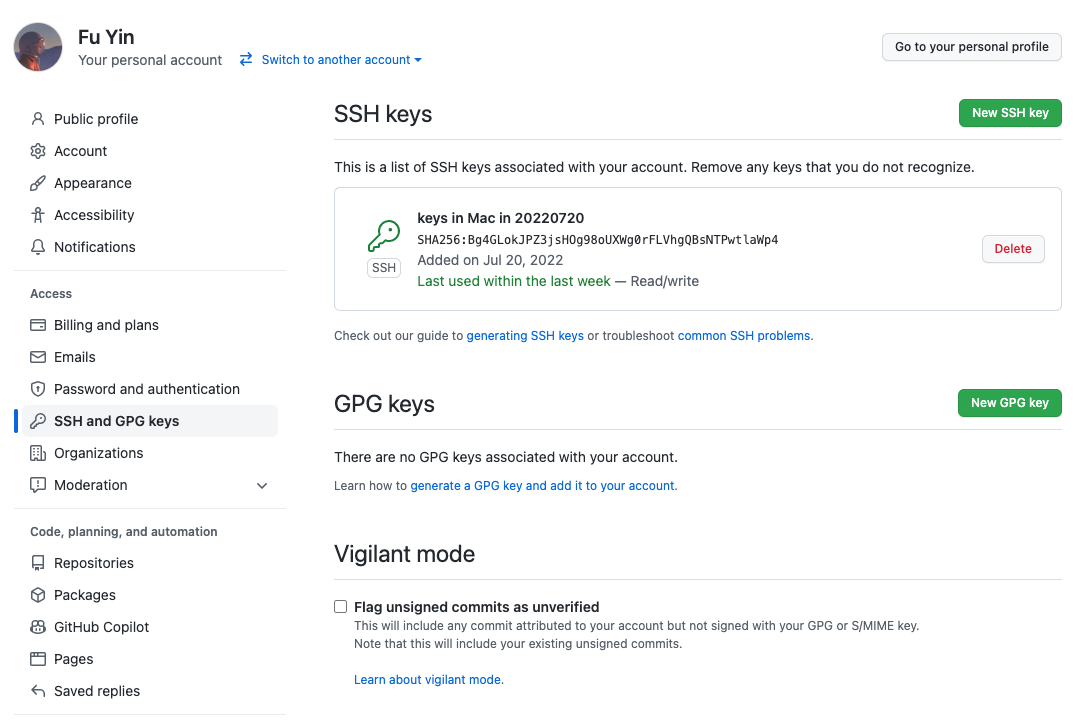
Fig. 4 SSH keys in Github#
Then check git SSH status
ssh -T git@github.com
Github IP in China#
Why is it very slow to access GitHub domain in China ?
Githubis not blocked in China, but due to the contamination ofDNS resolution, the access to Github domain is unusually slow in China. If domain name resolution points directly to theIP address of GitHub, that means the DNS resolution is bypassed, therefore the access to GitHub is accelerated.There are some organizations specialized in analyzing and maintaining the IP address of GitHub for China. You can query IP address of GitHub in real time by the
ipaddresswebsite, and add the latest IP address to the/etc/hostsfile.
We can update the IP address manually or automatically
Query the latest IP address of GitHub
usually query the following four domain names in ipaddress website.
Or you can connect the IP address with the ipaddress website to query directly:
Change the /etc/hosts file
After querying the IP, map the IP with the website address, and add the mapping relationship to the /etc/hosts file with sudo permission. For example:
vim /etc/hosts
# output with mapping format: [ip] [domainName]
199.232.69.194 github.global.ssl.Fastly.net
140.82.114.4 GitHub.com
185.199.108.153 assets-cdn.Github.com
140.82.114.9 codeload.Github.com
Refresh the /etc/hosts file
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
GitHub520 is a project that can real-time update the IP resolution of GitHub domain, the project server’s mirror website is HelloGitHub 镜像站. Run the following python code, then the IP resolution provided by GitHub520 will be obtained in real time, and the /etc/hosts file is automatically modified. The code is as follows:
"""
Created on Tue Feb 22 20:51:03 2022
@author: yinfu
"""
"""
##############################
## origin /etc/hosts file ##
##############################
#
# Host Database
#
# localhost is used to configure the loopback interface
# when the system is booting. Do not change this entry.
##
127.0.0.1 localhost
255.255.255.255 broadcasthost
::1 localhost
"""
from shutil import copyfile
import datetime
import os
import requests
import sys
class GithubHost:
winHostsPath='C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts'
macHostsPath='/etc/hosts'
hostsDic = {'win32':winHostsPath, 'darwin':macHostsPath}
dnsRefreshDic = {'win32':'ipconfig /flushdns', 'darwin':''}
githubHostUrl='https://raw.hellogithub.com/hosts'
googleHostUrl=''
def refreshHosts(self):
# 备份原hosts文件
hosts=self.hostsDic[sys.platform]
self.backUpHosts(srcfile=hosts)
# 获取并更新github新host内容
self.updateHosts(hosts, self.githubHostUrl, '# GitHub520 Host Start', '# GitHub520 Host End')
# 获取并更新google新host内容
# self.refreshHosts(hosts, self.googleHostUrl, '', '')
# 刷新
refreshCmd=self.dnsRefreshDic[sys.platform]
os.system(refreshCmd)
def updateHosts(self, hosts, hosturl, beginRowStr, endRowStr):
# 删除原有内容
self.removePartOfFile(hosts, beginRowStr, endRowStr)
self.addHostsFromURL(hosts, hosturl)
def removePartOfFile(self, file, beginRowStr, endRowStr):
lines = []
with open(file, 'r') as oldhosts:
lineInRange = False
for line in oldhosts:
# 如果在beginRowStr 与 endRowStr 之间的,就不记录在新文件中
if line.strip() == beginRowStr.strip():
lineInRange = True
if not lineInRange and line.strip() != '': # 删除空行
lines.append(line)
if line.strip() == endRowStr.strip():
lineInRange = False
with open(file, 'w') as newHosts:
for line in lines:
if len(line) != 0 and line is not os.linesep:
newHosts.write(line)
def backUpHosts(self, srcfile):
dstfile = srcfile + datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S')
copyfile(src=srcfile, dst=dstfile)
def addHostsFromURL(self, hostfile, hostsurl):
'''从github项目地址:读取最新的github的IP记录'''
with open(hostfile, 'a+') as fw:
# 字符串给出当前平台使用的行终止符。例如,Windows使用'\r\n',Linux使用'\n'而Mac使用'\r'。
# fw.write(os.linesep)
fw.write(requests.get(hostsurl).text.strip())
if __name__ == '__main__':
GithubHost().refreshHosts()
Note
sudo permission is required to modify /etc/hosts. Make sure to back up the original /etc/hosts. The script will update the content between the line from # GitHub520 Host Start to # GitHub520 Host End, without deleting or modifying anything else.
The following is an example of a modified /etc/hosts file:
##
# Host Database
#
# localhost is used to configure the loopback interface
# when the system is booting. Do not change this entry.
##
127.0.0.1 localhost
255.255.255.255 broadcasthost
::1 localhost
# MacWk.com Hosts Start
# Macs Fan Control
127.0.0.1 crystalidea.com
127.0.0.1 www.crystalidea.com
127.0.0.1 v3pro.crystalidea.com
# MacWk.com Hosts End
# GitHub520 Host Start
140.82.113.4 alive.github.com
140.82.113.4 live.github.com
18.232.140.192 github.githubassets.com
140.82.113.4 central.github.com
44.201.249.207 desktop.githubusercontent.com
140.82.113.4 assets-cdn.github.com
44.206.232.135 camo.githubusercontent.com
151.101.1.6 github.map.fastly.net
151.101.1.6 github.global.ssl.fastly.net
140.82.113.4 gist.github.com
185.199.108.153 github.io
140.82.113.4 github.com
192.0.66.2 github.blog
140.82.113.4 api.github.com
18.204.44.248 raw.githubusercontent.com
54.163.208.41 user-images.githubusercontent.com
44.204.67.163 favicons.githubusercontent.com
44.192.65.19 avatars5.githubusercontent.com
18.208.135.184 avatars4.githubusercontent.com
54.175.3.163 avatars3.githubusercontent.com
3.239.50.191 avatars2.githubusercontent.com
54.87.18.202 avatars1.githubusercontent.com
54.197.52.125 avatars0.githubusercontent.com
3.236.14.33 avatars.githubusercontent.com
140.82.113.4 codeload.github.com
72.21.206.80 github-cloud.s3.amazonaws.com
72.21.206.80 github-com.s3.amazonaws.com
72.21.206.80 github-production-release-asset-2e65be.s3.amazonaws.com
72.21.206.80 github-production-user-asset-6210df.s3.amazonaws.com
72.21.206.80 github-production-repository-file-5c1aeb.s3.amazonaws.com
185.199.108.153 githubstatus.com
64.71.144.211 github.community
23.100.27.125 github.dev
140.82.113.4 collector.github.com
184.72.161.117 pipelines.actions.githubusercontent.com
44.193.198.252 media.githubusercontent.com
54.196.61.168 cloud.githubusercontent.com
3.236.14.33 objects.githubusercontent.com
13.107.213.51 vscode.dev
# Update time: 2022-07-15T22:10:03+08:00
# Update url: https://raw.hellogithub.com/hosts
# Star me: https://github.com/521xueweihan/GitHub520
# GitHub520 Host End
Note
The IP address of the Github changes frequently, and we should update /etc/hosts file when it slows down again.
Why git push with error? OpenSSL SSL_connect…
The following error may occur when use git push with using an agent refer to SSL_connect: SSL_ERROR_SYSCALL…:443
Push failed: Failed with error: unable to access 'https://github.com/weidongcao/bigdata/':
OpenSSL SSL_connect: SSL_ERROR_SYSCALL in connection to github.com:443
Git supports 3 network protocols:
git://...ssh://...http://...
The SSH tunnel is supposed to be used when use git push command. However, if the http proxy is set, the http proxy will be used. Therefore, the above error occurs. The solution is to cancel the http proxy:
git config --global --unset http.proxy
Manual#
creating a repository#
Init Locally
Check that init locally is not recommended.
Initializes a local repository and make some commit as following:
git init
git add .
git commit -m 'first commit'
Create an empty repository in GitHub, then associate the remote repository with the local repository to keep synchronization as following,
originis the name of the remote repository which can be replaced arbitrarily:
git remote add origin git@github.com:your_github_name/repo_name.git
Since the remote library is empty, the first time we push the
mainbranch, we should add the-uparameter. Git will not only push the contents of the local main branch to the new remote main branch, but also associate the local main branch with the remote main branch, which can simplify the command in the future when usegit pushorgit pull
git push -u origin main
Now the following commands can be used:
# git push
git push origin main
# check the origin repository address
git remote -v
# if you want to remove the current repository address
git remote rm origin
Init Remotely
Assuming you have created a remote repository on GitHub, you can use
sshforgit clone, which is fast thanhttpsin China.
git clone git@github.com:your_Github_name/reop_name.git
Init Submodule
If your code needs to use other package, which is located on GitHub. You need to use
gitto initialize and update.git submodule init xxxwill download some info provided by.gitmodulesfile to fill.git/config. Then usegit updateto clone those code. Here is an example refer to https://www.codenong.com/44366417/.
For example a
.gitmodulesfile contains three submodules to use:
[submodule "pygments-style-algforopt"]
path = style
url = https://github.com/sisl/pygments-style-algforopt.git
branch = master
[submodule "pygments-julia"]
path = lexer
url = https://github.com/sisl/pygments-julia.git
branch = master
[submodule "juliaplots.sty"]
path = juliaplots.sty
url = https://github.com/sisl/juliaplots.sty.git
branch = master
If we only need to use the
pygments-juliaandjuliaplots.stycode, which means that do not require clone and checkoutpygments-style-algforopt, we can use
git submodule init pygments-julia juliaplots.sty
Then run the following command to clone and check them
git submodule update
add, commit and push#
Add changes to the local repository.
# Add the changes to the Index
git add <filename>
# Add all changes at once
git add .
# check status
git status
# Add the changes from Index to local Repository
git commit -m "your comment"
Push the last changes in the
Local Repositoryto theRemote Repositoryin github.
git push origin main
If you need to connect your local repository to a remote repository, use the following command
git remote add origin <server>
branch, merge and diff#
Create a new branch and switch to it
# new branch's name is feature
git switch -c feature_x # or: git checkout -b feature_x
# create the dev branch of the remote origin to the local
git checkout -b dev origin/dev
# switch to main branch
git switch main # or: git checkout main
Delete a branch
# delete a local branch
git branch -d <branch-name>
# delete a remote branch
git push origin --delete <branch-name>
Compare 2 branches
# show a file list with difference between 2 branches
git diff branch1 branch2 --stat
# show detailed differences for the specified file
git diff branch1 branch2 /path/to/file
# show the detailed differences of all the different files between 2 branches
git diff branch1 branch2
Merge 2 branches
# merge the contents of the dev branch under the main branch
git merge dev
# the '--no-ff' option disables fast-forward mode, and '-m' records the merge as a commit
git merge --no-ff -m "merge dev --add new blog-1" dev
pull = fetch + merge#
If the team is developing on the
dev branchand a teammate commits a new commit todev, we need topullthe commit from GitHub to our localdev branchbefore developing
# specify the link between the local dev branch and the remote origin's dev branch
git branch --set-upstream-to=origin/dev dev
# pull code
git pull
Note
git pull = git fetch + git merge, and git fetch will only pull remote code to local repo and do not merge it.
tag#
# tag the current branch with v1.0
git tag v1.0
# show all the tags
git tag
# show the tag v0.9's information
git show v0.9
# tag a previous commit,f52c633 is the 'commit id'
git tag v0.9 f52c633
# create a tag with instructions,'-a' add tga ,'-m' add instructions
git tag -a v0.1 -m "version 0.1 released" 1094adb
# delete a tag
git tag -d v0.1
# push the tag to remote
git push origin v1.0
# Push all local tags that have not been pushed to the remote at one time
git push origin --tags
# delete a remote tag (make sure that you have deleted the local tag before)
git push origin :refs/tags/v0.9
log#
git log --graph --pretty=oneline --abbrev-commit
git log --pretty=oneline --abbrev-commit
git log --pretty=oneline
# check the latest commit
git log -1
delete files#
delete one file
# delete test.txt from repo and commit
git rm test.txt
git commit -m "remove test.txt"
# use 'rm' delete,then 'git add' and 'git commit'
rm text.txt
git add .
git commit -m "remove test.txt"
delete untracked files from
.gitignore
# delete untracked files
git clean -f
# delete untracked files and their directory
git clean -fd
# ? cautious
git clean -xfd
it is highly recommended to add the
-nparameter to see which files will be deleted first to prevent the deletion of important files by mistake
git clean -nxfd
git clean -nf
git clean -nfd
How to remove all ‘.DS_Store’ files?
We need to remove those
.DS_Storefiles from the directory which already added to git. Use the following command which will go through all the folders in your directory, and remove those files from git.
find . -name .DS_Store -print0 | xargs -0 git rm -f --ignore-unmatch
Add
.DS_Storeto the file.gitignore, which can be found at the top level of your repository (or create the file if it isn’t there already). You can do this easily with this command in the top directory:
echo .DS_Store >> .gitignore
Last step, we need to actually commit the
.gitignorefile.
git status
git add .gitignore
git commit -m '.DS_Store banished!'
Clean the files recorded in
.gitignore
git clean -X -f
版本回退 (working…)#
Warning
最新版本的git已经使用git restore 代替了原来的reset和checkout命令了
在 Git 中,用HEAD表示当前版本, 上一个版本是HEAD^,上上一个版本是HEAD^^,往上100个版本HEAD~100。但推荐使用commit id来退回版本:
# 退回到上一个版本
git reset --hard HEAD^
# 首先查看历史 commit 的 id
git log
# 例如发现 id 是 1094a,退回到该版本
git reset --hard 1094a
Note
Git的版本回退速度非常快,因为Git在内部有个指向当前版本的HEAD指针,当你回退版本的时候,Git仅仅是把HEAD从指向append GPL
现在退回到过去的版本了,想回到未来的版本:
# 要重返未来,用'git reflog'查看命令历史,以便确定要回到未来的哪个版本
git reflog
# 例如发现未来的 id 是 1094a,退回到该版本
git reset --hard 1094a
撤销修改 (working…)#
Warning
需要替换成最新版本的 git restore
git checkout -- xx.txt
figure#
Link from git-tips project.